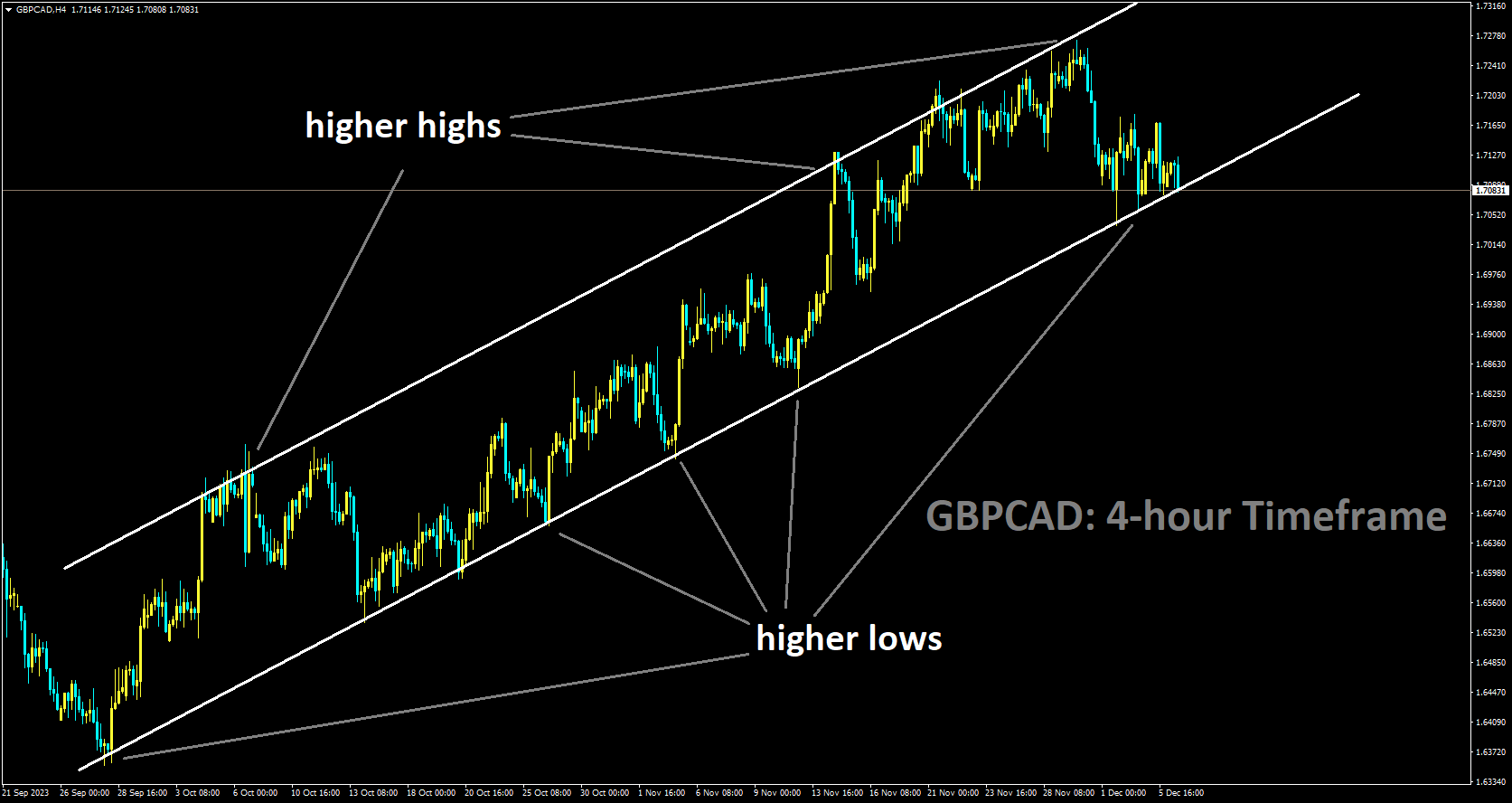
GBPCAD is moving in a ascending channel and the market has reached higher low area of channel
The Bank of Canada intends to keep interest rates steady at 5.00% next week. The Governor of the Bank of Canada has emphasized the sufficiency of the current rate levels to control inflation within the economy. The Q3 decline in Canada’s GDP indicates that the recent rate hike represents the highest point for interest rates in Canada. Elevated interest rates are exerting significant pressure on job demand and businesses.
Economists surveyed by Reuters predict that the Bank of Canada (BoC) will initiate interest rate cuts in the second quarter of 2024. The rationale behind this forecast is a combination of slowing inflation and a decelerating economy. These experts anticipate that the BoC will lower its base borrowing costs by at least one percentage point by the end of 2024.
The consensus among these economists underscores a shift in the central bank’s monetary policy. Throughout 2022 and into 2023, the BoC steadily increased interest rates. However, as economic conditions evolve, central banks must adjust their strategies to maintain price stability and support sustainable growth.
Central Bank’s Delicate Balancing Act
BoC Governor Tiff Macklem recently addressed the nation in a speech, shedding light on the current state of interest rates and their potential trajectory. Macklem acknowledged that the excessive demand that characterized the earlier part of 2022 has dissipated. Weak economic growth is also expected to persist. While these factors suggest that further interest rate hikes might not be necessary, Macklem emphasized that it was not yet time to consider rate cuts.

Macklem’s comments highlight the complex and nuanced nature of central bank decision-making. Balancing the need to combat inflation with the risk of stifling economic growth requires careful analysis and consideration. It’s a delicate balancing act that central banks around the world must perform.
Economic Conditions and Expectations
To better understand the central bank’s current stance, let’s examine the economic conditions in Canada. The nation’s economy experienced modest growth in the last quarter, with a 0.2% annualized rate following a contraction of 0.2% in the previous quarter. While this growth is not substantial, it suggests a level of resilience in the face of economic headwinds.
The most significant development, however, was the notable drop in inflation. Inflation fell from a peak of 8.1% in June 2022 to 3.1% last month. This decrease in inflation is a crucial factor driving expectations of interest rate cuts. When inflation is high, central banks often raise interest rates to cool down the economy and keep prices stable. Conversely, when inflation eases, central banks may consider reducing interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
Expert Opinions on Interest Rate Changes
A Reuters poll conducted from November 27 to 30 revealed that 25 out of 26 economists anticipate that the BoC will maintain its main policy rate at 5.0% until at least the end of March. This aligns with expectations for the U.S. Federal Reserve, which often influences global economic trends.
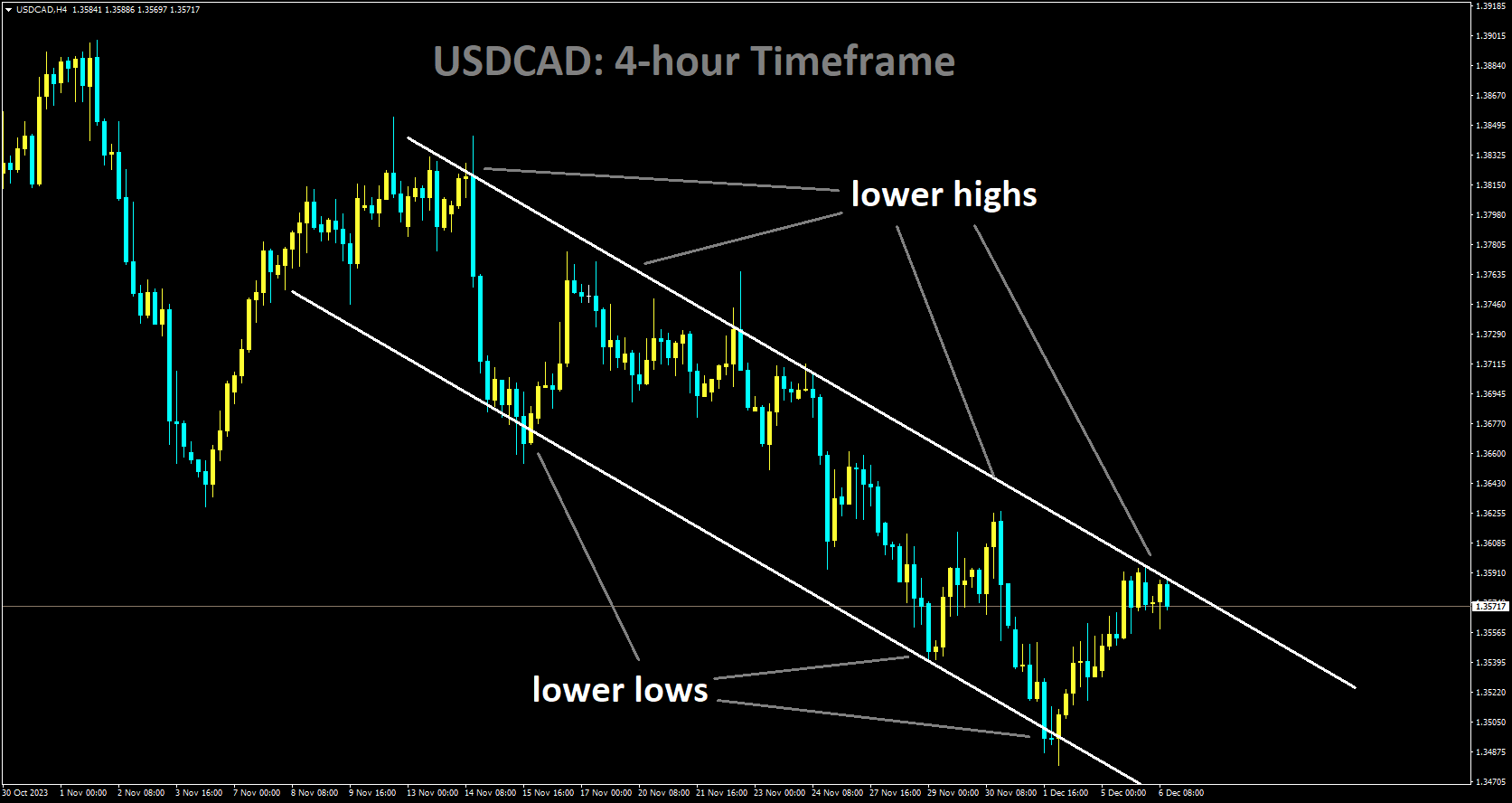
USDCAD is moving in a descending channel and the market has reached the lower high area of the pattern
Barclays stands out as the lone dissenter in the poll, expecting one more 25 basis point rate hike in January. The disparity between Barclays’ prediction and the consensus reflects the uncertainty and complexity of the current economic environment.
Interest rate futures, on the other hand, are pricing in the first rate cut in March, which is earlier than the poll’s prediction. This difference in market expectations versus economists’ consensus demonstrates the dynamic nature of financial markets and their role in influencing interest rate decisions.
Impact on the Housing Market and Homeownership
The potential interest rate cuts raise questions about their implications for the housing market and aspiring homeowners. Approximately 60% of mortgage holders are yet to renew their home loans at higher rates, making this a crucial concern for many Canadians.
If interest rates are cut, it could lead to lower borrowing costs for homebuyers, potentially boosting demand in the housing market. Lower rates may make it more affordable for individuals and families to purchase homes, which could have a positive impact on the real estate sector.
However, there is a flip side to this equation. Lower interest rates might also lead to increased competition in the housing market, potentially driving up property prices. Additionally, it could encourage speculative buying, which might lead to concerns about a housing bubble.

A separate poll of 11 property analysts conducted from November 15 to 30 forecasted that average home prices, which surged over 50% during the pandemic, would stagnate in 2024. This follows a decline of 3.3% in prices this year. The property analysts’ predictions provide insights into the nuanced dynamics of the housing market in response to potential interest rate cuts.
The Effect of Rate Hikes and Stock Market Performance
During the Bank of Canada’s rate hike cycle, interest rates reached as high as 5%. Such sharp rate hikes significantly increased mortgage interest payments for Canadian households. While higher interest rates brought higher income to banks, they also increased credit risk for borrowers.
Fear overpowered optimism in financial markets, and bank and lending stocks faced downward pressure throughout the rate hike cycle. Rising interest expenses affected companies with large debt burdens, prompting some to slash dividends in order to prioritize mortgage payments.
Moreover, when a significant portion of individuals’ income goes toward servicing debt, they tend to spend less on discretionary items or postpone their purchases. This decline in consumer demand had a ripple effect on various sectors of the economy. For example, stocks of discretionary items like automobiles experienced a downturn due to decreased consumer spending.
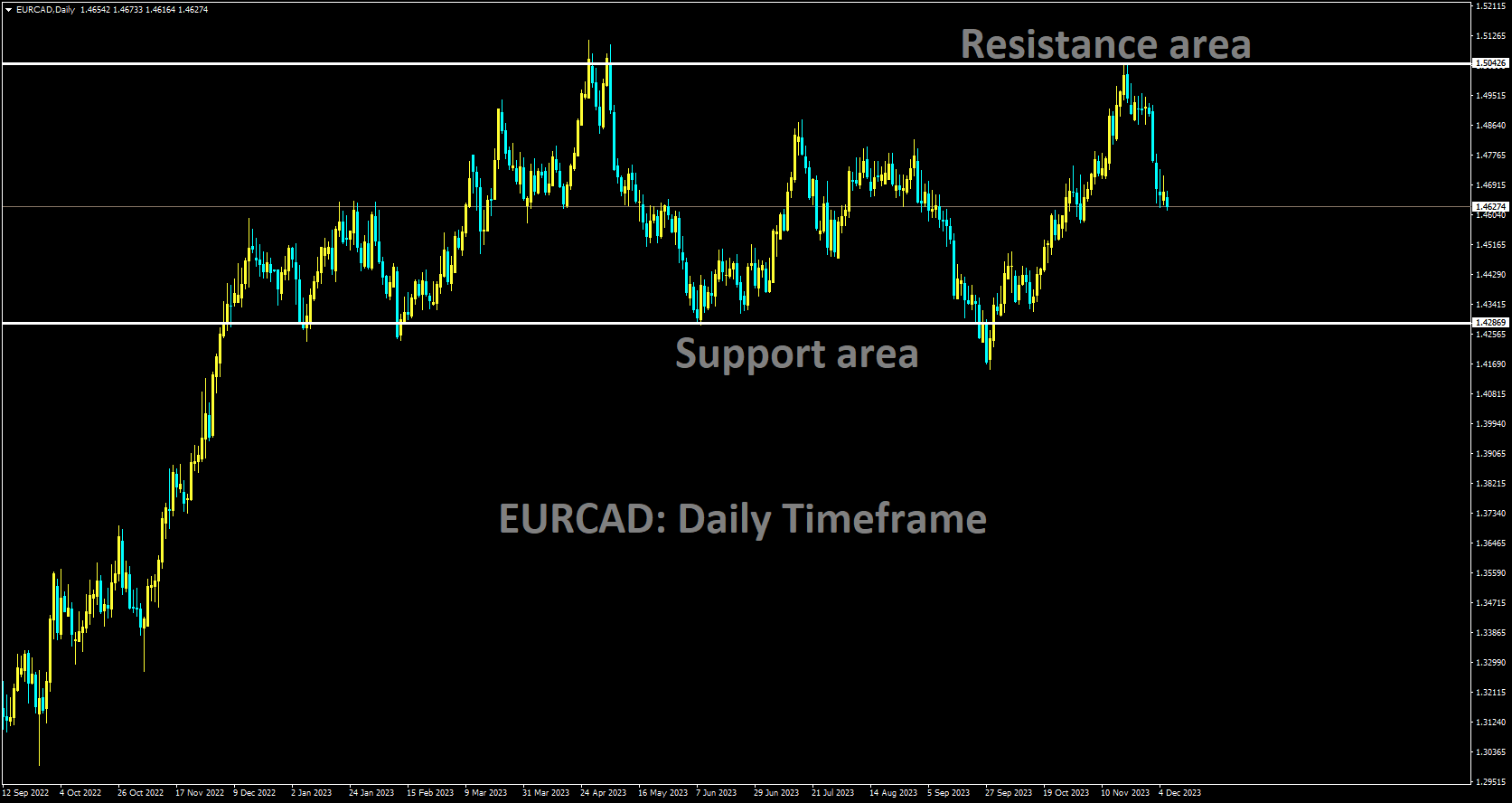
EURCAD is moving in a box pattern and the market has fallen from resistance area
Now that Canada’s inflation has eased to 3.1% in October, the Bank of Canada has paused interest rate hikes. The rate has remained unchanged at 5% since July. As a result, some optimism has emerged regarding potential interest rate cuts in early 2024. This optimism is expected to gain prominence following the December 6 meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee. Some strong upside momentum is likely in early December, and smart investors are considering stocks that could benefit from interest rate cuts.
The Current Interest Rate Landscape in Canada
Currently, the Bank of Canada is holding its policy rate at 5%, reflecting its cautious approach to monetary policy. While other central banks worldwide have taken various approaches to managing their interest rates, the BoC’s decision to maintain the rate indicates a willingness to assess the economic situation carefully before making further adjustments.
It’s important to note that the central bank’s decisions are not static. They evolve in response to changing economic conditions, both domestic and international. The December 6 meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee could provide critical insights into the central bank’s thinking and its potential actions regarding interest rates.
Factors Influencing Canadian Interest Rates
Interest rates in Canada are subject to various factors, including inflation, market conditions, and government policies. Understanding these variables is essential for individuals, businesses, and investors to make informed financial decisions.
Inflation: Inflation is one of the most significant factors influencing interest rates. When inflation is high, central banks often raise interest rates to curb inflationary pressures. Conversely, when inflation is low or declining, central banks may consider lowering interest rates to stimulate economic activity.

Market Conditions: The overall economic environment and financial market conditions play a crucial role in interest rate decisions. Factors such as economic growth, employment levels, and global economic trends can influence central bank policies.
Government Policies: Government regulations and fiscal policies can impact interest rates. For example, government spending and taxation policies can affect the overall economic environment, which, in turn, may influence interest rate decisions.
Global Economic Trends: Canada is part of the global economy, and international factors can influence its interest rates. Changes in global economic conditions, trade policies, and geopolitical events can have repercussions on Canadian interest rates.
Central Bank Mandate: The mandate of the central bank, in this case, the Bank of Canada, is to maintain price stability and support economic growth. The central bank’s actions are guided by these objectives.
Banking Industry: The health of the banking and financial sector can also influence interest rates. A stable and robust financial system can provide the central bank with more flexibility in its rate-setting decisions.
Understanding these factors can help businesses and individuals anticipate potential changes in interest rates and make financial decisions accordingly.
Potential Changes in Canada’s Interest Rate in 2024
Economists predict that the Bank of Canada will reduce interest rates in 2024, potentially delivering 100 basis points of rate cuts throughout the year. This prediction is based on a combination of factors, including easing inflation and a weaker economic outlook.
The timing of these rate cuts, expected to start in the second quarter, will depend on evolving economic conditions and the central bank’s assessment of the need for monetary stimulus. If the BoC follows through with rate cuts, it could have broad implications for borrowing costs, consumer spending, and economic growth.
Factors Impacting Borrowing Rates
Different types of loans, such as car loans, home loans, and mortgages, are affected differently by interest rate adjustments. Understanding how these changes in interest rates impact borrowing costs is essential for consumers and businesses alike.
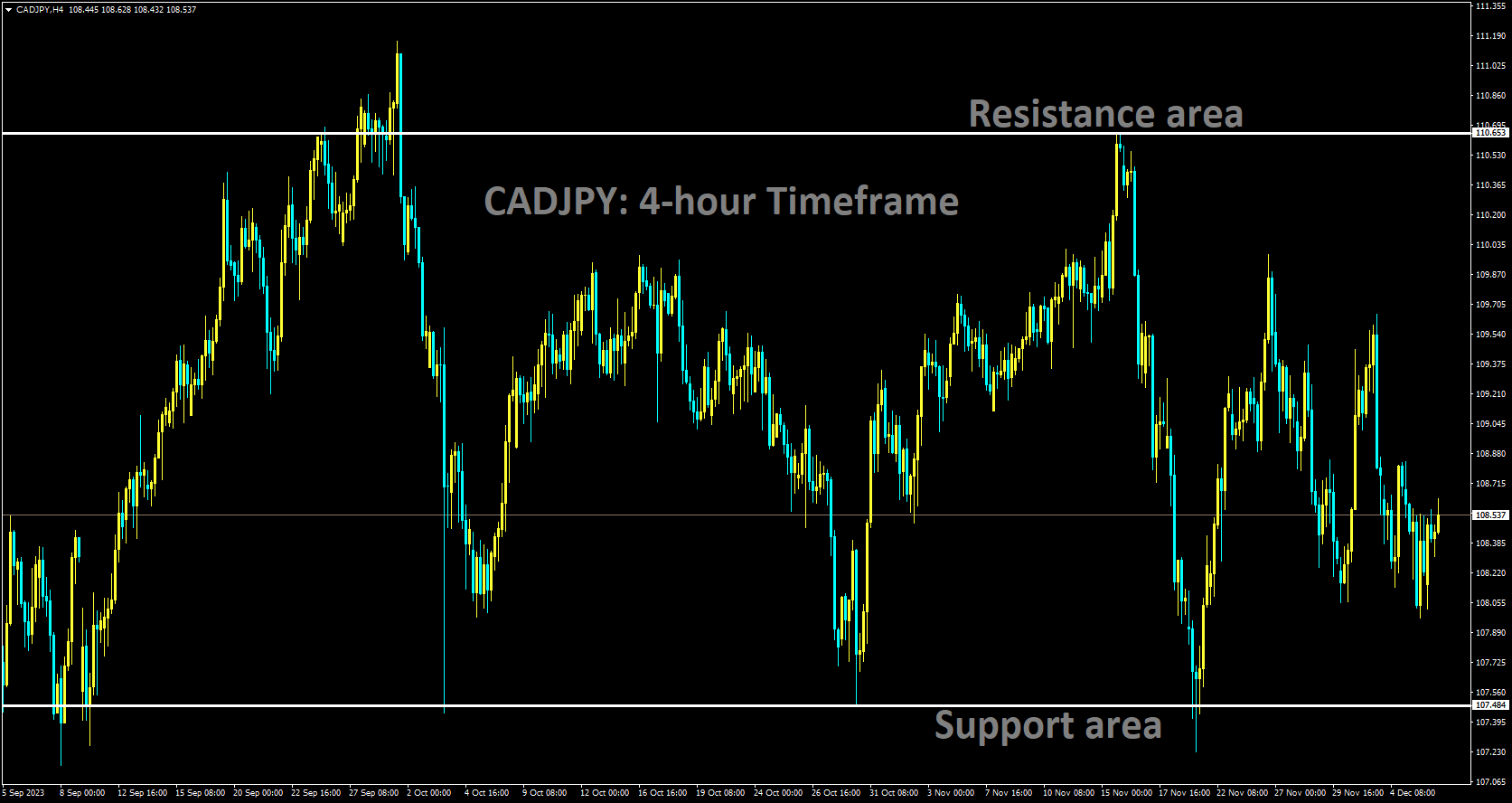
CADJPY is moving in a box pattern and the market has rebounded from the support area
Mortgages: Mortgage rates are closely tied to central bank policy rates. When policy rates are reduced, mortgage rates tend to follow suit, making it more affordable for individuals to finance home purchases or refinance existing mortgages. Conversely, when policy rates rise, mortgage rates can increase, potentially impacting home affordability.
Car Loans: Car loans are influenced by both policy rates and market conditions. When policy rates are lowered, it can lead to lower interest rates on car loans, making vehicle financing more attractive. However, market conditions, lender policies, and individual credit profiles also play a role in determining car loan rates.
Home Equity Loans: Home equity loan rates may also respond to changes in policy rates. A lower policy rate can translate into lower interest costs for homeowners looking to access the equity in their homes. This can be particularly relevant for home renovations or debt consolidation.
Credit Cards and Personal Loans: Interest rates on credit cards and personal loans are often influenced by policy rates but can also vary based on individual creditworthiness. When policy rates are reduced, it may result in lower interest costs for credit card balances and personal loans.
Business Loans: Business loans, including lines of credit and term loans, are subject to various factors, including policy rates, creditworthiness, and business risk. Changes in policy rates can impact the overall cost of borrowing for businesses, affecting their investment decisions and growth prospects.
Understanding how changes in interest rates affect borrowing costs is crucial for individuals and businesses when making financial decisions. Lower interest rates can lead to cost savings and potentially stimulate economic activity, while higher rates may increase the cost of borrowing and impact spending and investment.
Government Regulations and Interest Rate Determination
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping interest rates in Canada. These policies are designed to maintain economic stability, support economic growth, and ensure the overall well-being of the country’s financial system.

Monetary Policy: The Bank of Canada is responsible for implementing monetary policy in Canada. Its primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which involves targeting a specific level of inflation. The central bank uses its policy rate to influence borrowing costs and economic activity. Changes in the policy rate can impact interest rates throughout the economy.
Fiscal Policy: Fiscal policies, including government spending and taxation, can also influence interest rates. Expansionary fiscal policies, such as increased government spending, can stimulate economic growth, potentially leading to higher interest rates if they fuel inflationary pressures. Conversely, contractionary fiscal policies may be implemented to cool down an overheated economy, potentially leading to lower interest rates.
Regulatory Framework: The government establishes regulations and oversight mechanisms to ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system. These regulations govern financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, and other lenders. They also include measures to protect consumers and investors.
Government Debt Issuance: The government’s issuance of bonds and other debt securities can impact interest rates. When the government increases its borrowing through bond issuance, it can put upward pressure on interest rates in the broader financial markets.
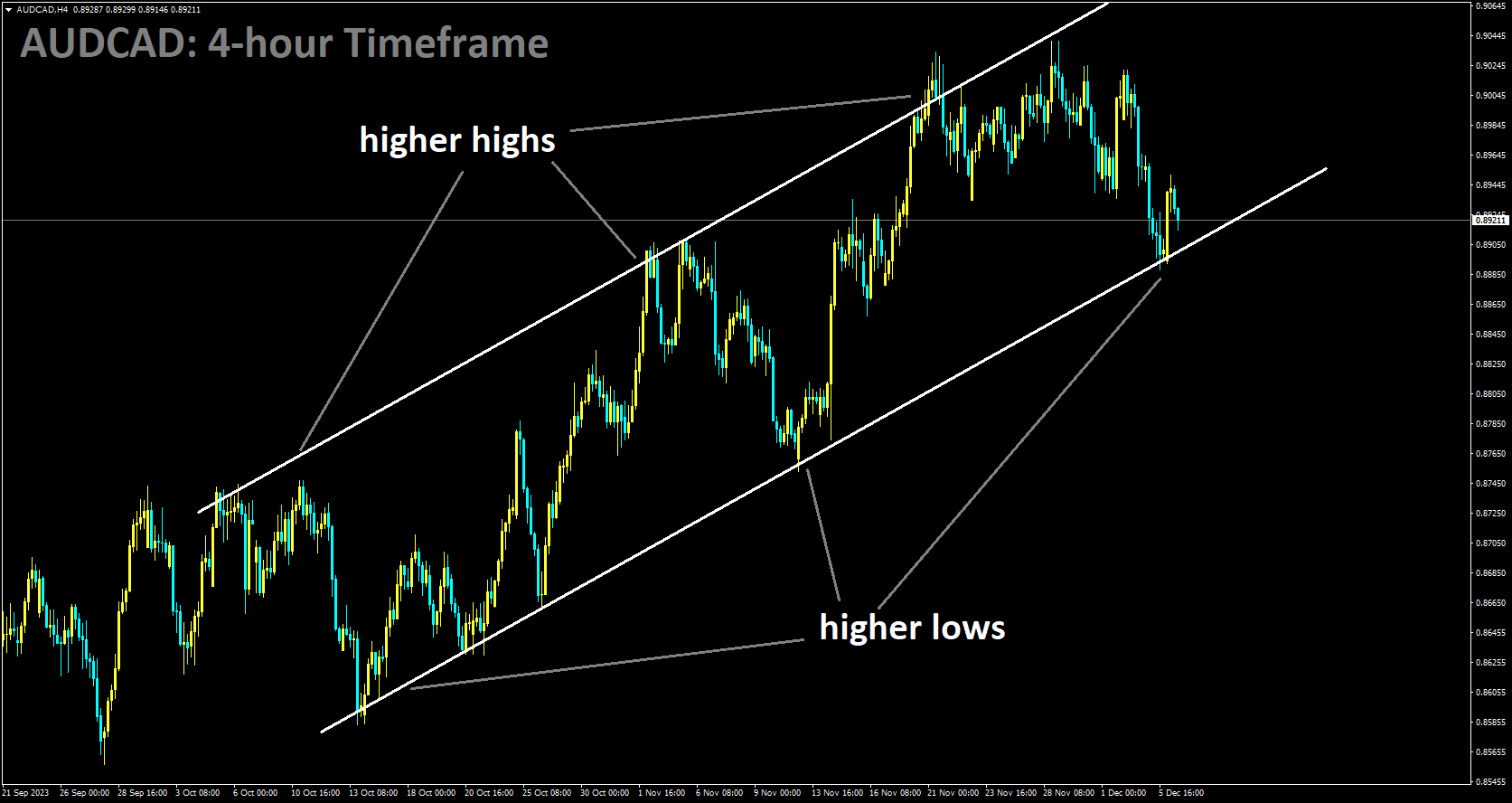
AUDCAD is moving in a ascending channel and the market has reached the higher low area of the channel
Foreign Exchange Policy: Government policies related to the Canadian dollar’s exchange rate can also influence interest rates. A weaker Canadian dollar can put upward pressure on interest rates by potentially increasing the cost of imported goods and inflation.
Global Economic Environment: Canada’s economy is interconnected with the global economy. Changes in global economic conditions, trade policies, and geopolitical events can have indirect effects on Canadian interest rates.
Financial Stability: Government policies are designed to maintain financial stability and prevent systemic risks. This includes measures to address issues related to housing markets, banking sector health, and financial market stability.
Overall, government policies and regulations are critical for shaping the macroeconomic environment and influencing interest rate decisions. Central banks like the Bank of Canada work in tandem with government policies to achieve economic stability and growth.
In conclusion, the Bank of Canada’s interest rate decisions are influenced by a complex interplay of economic conditions, inflation trends, market dynamics, and government policies. As economists forecast interest rate cuts in 2024, it is essential to recognize the potential impact of these changes on the housing market, borrowing costs, and overall economic activity. Moreover, understanding the factors influencing Canadian interest rates provides individuals, businesses, and investors with valuable insights to make informed financial decisions in an ever-evolving financial landscape.
🔥 Stop Trading all the time, trade markets only at the best setups with Premium or VIP plan
🎁 60% CYBER MONDAY OFFER 🎁 for Trading Signals 😍 GOING TO END – Get now: https://forexfib.com/offer/