EURO: Eurozone inflation slows to 2.4% YoY in March, missing 2.6% forecast
The Euro zone CPI came at 2.4% in March month versus 2.6% increase in February month.Core CPI came at 2.9% in March month versus February 3.1% increased. Service inflation recorded highest in march month, other sectors contributed lesser in the inflation area compared to previous month. Euro pairs mostly down against counter pairs after the reading published.
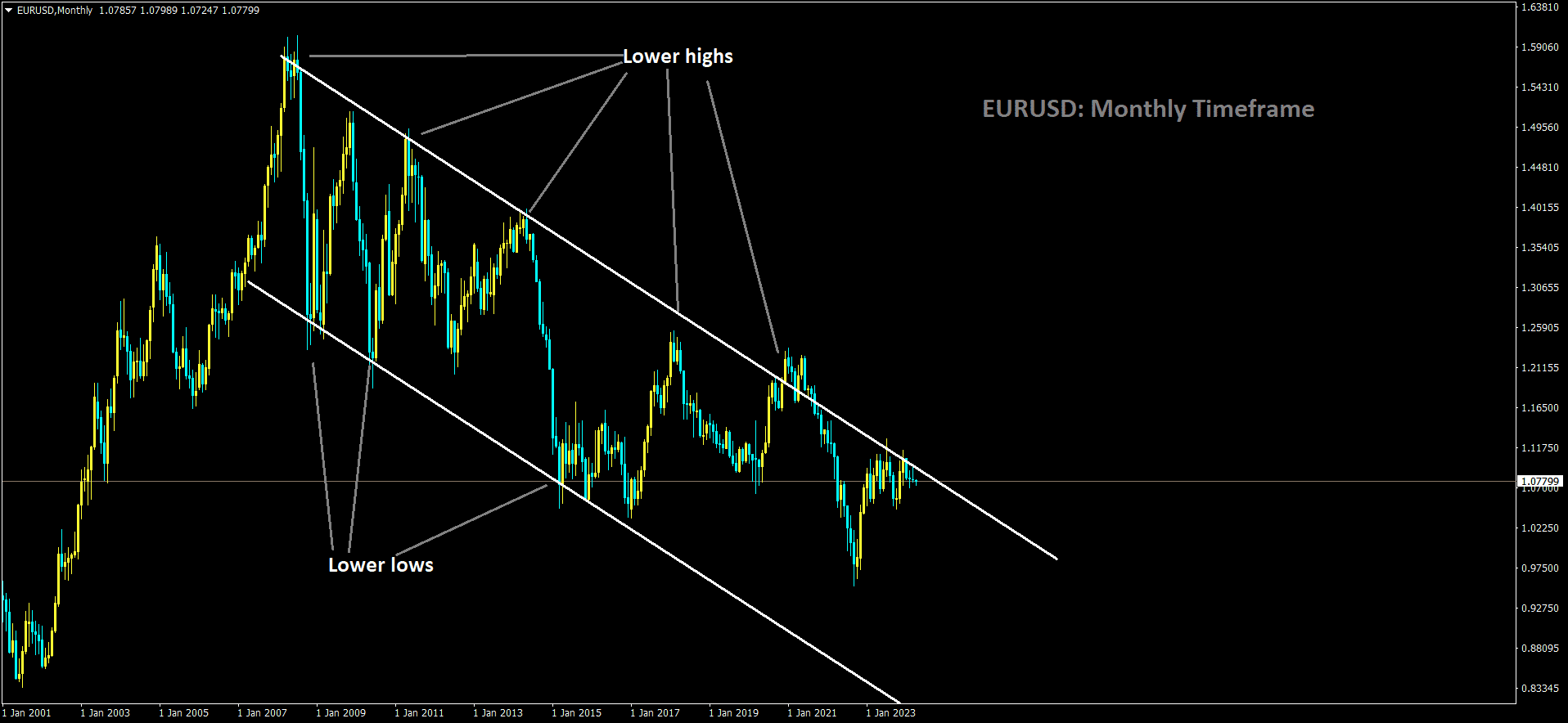
EURUSD is moving in Descending channel and market has reached lower high area of the channel
In March, the annual Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) for the Eurozone increased by 2.4%, marking a slowdown from the 2.6% growth observed in February, as per data released by Eurostat. This figure fell short of the market’s expectation, which had anticipated a 2.6% rise.
Additionally, the Core HICP inflation, excluding volatile food and energy prices, softened to 2.9% year-on-year in March, down from the 3.1% increase recorded in February and below the estimated 3.0%.
On a monthly basis, the HICP for the Eurozone rose by 0.8% in March, compared to a 0.6% increase in February. Meanwhile, the core HICP inflation increased by 1.1% month-on-month in March, surpassing the 0.7% rebound seen in the previous month.
The European Central Bank (ECB) targets an inflation rate of 2.0%, and fluctuations in the Eurozone’s HICP inflation data significantly influence market expectations regarding the ECB’s future interest rate decisions.

Key insights from the Eurozone inflation report provided by Eurostat indicate that services are expected to have the highest annual rate of inflation in March, at 4.0%, remaining stable compared to February. This is followed by food, alcohol & tobacco, with an inflation rate of 2.7%, down from 3.9% in February. Non-energy industrial goods saw an inflation rate of 1.1%, down from 1.6% in February, while energy prices declined by 1.8%, an improvement from the 3.7% decrease in February.
In a separate report, the Eurozone Unemployment Rate remained steady at 6.5% in February, unchanged from the revised figure for January.
EURO: Eurozone inflation unexpectedly softens; core rate hits two-year low
The Euro zone CPI came at 2.4% in March month versus 2.6% increase in February month.Core CPI came at 2.9% in March month versus February 3.1% increased. Service inflation recorded highest in march month, other sectors contributed lesser in the inflation area compared to previous month. Euro pairs mostly down against counter pairs after the reading published.
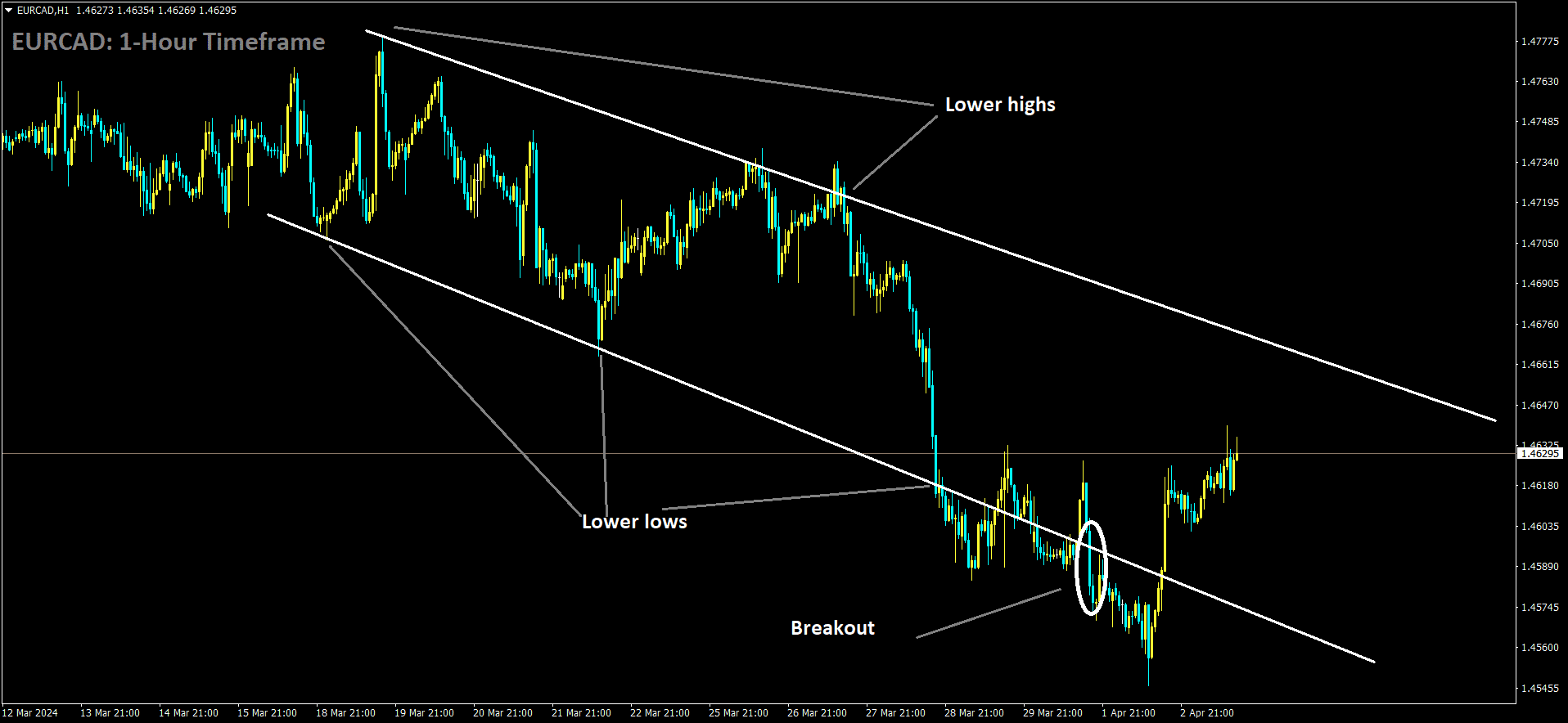
EURCAD is moving in Descending channel and market has rebounded from the lower low area of the channel
In March, inflation within the eurozone unexpectedly decelerated, with the core rate plunging to its lowest point in over two years, signifying a continued easing of price pressures across the single-currency area.
Eurostat reported a year-on-year dip in the eurozone’s harmonized consumer price index to 2.4% last month, down from February’s 2.6%, catching economists off guard, as they had predicted no change. This matches the rate observed in November 2023, marking the lowest level recorded since July 2021.

Simultaneously, the core rate, which excludes volatile components like food and energy, also moderated, slipping to 2.9% from 3.1%, falling below the anticipated 3.0% and marking the lowest reading since February 2022.
Meanwhile, in February, the eurozone’s unemployment rate remained steady at 6.5%, unchanged from the revised figure for January, which was revised upward from 6.4% to 6.5%. This reading was contrary to the consensus forecast of 6.4%.
Analysts at Rabobank interpreted the data as a sign that conditions for a potential interest-rate cut by the European Central Bank (ECB) in June are maturing. They noted that the Eurozone’s March CPI inflation estimate of 2.4% year-on-year is likely to cement market expectations for a June ECB rate cut.
EURO: Eurozone inflation nears 2%, eyes on June cut
The Euro zone CPI came at 2.4% in March month versus 2.6% increase in February month.Core CPI came at 2.9% in March month versus February 3.1% increased. Service inflation recorded highest in march month, other sectors contributed lesser in the inflation area compared to previous month. Euro pairs mostly down against counter pairs after the reading published.
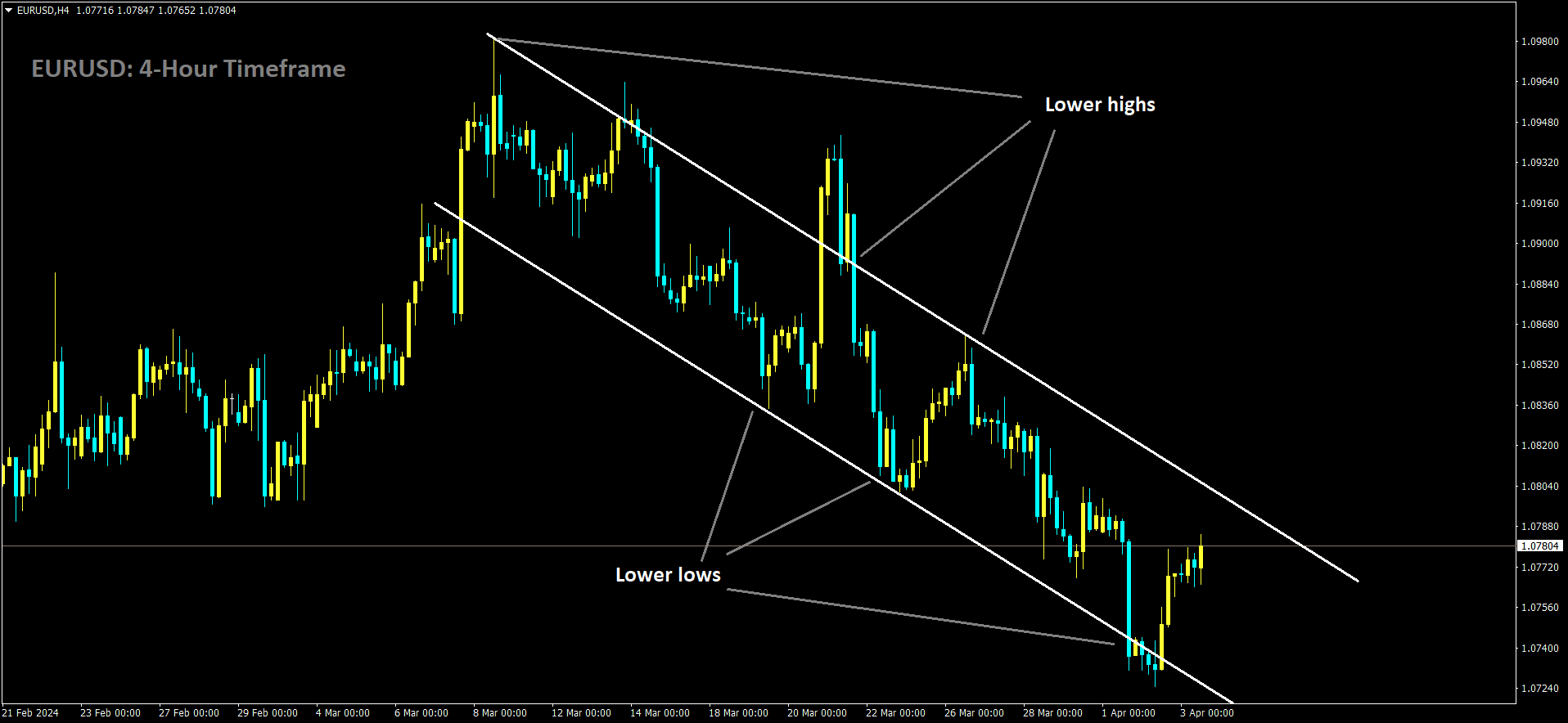
EURUSD is moving in Descending channel and market has rebounded from the lower low area of the channel.
Euro-area inflation slowed more than anticipated, reinforcing expectations for an interest-rate cut by the European Central Bank (ECB) in June.
According to Eurostat data, consumer prices in the eurozone increased by 2.4% annually in March, down from 2.6% in February. This figure aligns with Bloomberg Economics’ Nowcast model, while analysts had forecasted a 2.5% rise. The core inflation rate, which excludes volatile items like food and energy, also eased more than expected, falling to 2.9%.
The report underscores the ECB’s aim to bring inflation back to its 2% target, potentially allowing for the relaxation of some previously implemented measures. ECB President Christine Lagarde has hinted at a rate cut in June, pending updated forecasts and wage growth data for the early part of the year.
Most members of the ECB’s Governing Council, including representatives from major eurozone economies like Germany, France, and Spain, appear to support the June timeline for rate cuts. Economists and financial markets are in agreement, suggesting that significant developments would be needed to alter this course.
Following the release of the inflation report, traders maintained expectations for rate cuts this year, pricing in three quarter-point reductions starting in June, with a probability of a fourth cut at around 60%. This contrasts with the expectations before last month’s monetary policy decision, where up to four cuts were priced in.
While recent events such as shipping disruptions in the Middle East and the collapse of a bridge in Baltimore have had minimal impact on eurozone inflation, rising wages within the region could potentially fuel price increases. ECB Chief Economist Philip Lane emphasizes the need for wage growth to moderate further before considering reversing past rate hikes.
Despite some moderation observed in a key compensation gauge at the end of 2023, salaries in the eurozone continue to grow by more than 4%, contributing to inflationary pressures, particularly in the services sector. In March, inflation in the services sector remained at 4%, while the rate for non-energy industrial goods fell to 1.1%.
Inflation trends vary across the eurozone, with Spain experiencing an acceleration in inflation after the government removed some energy cost support measures, while Germany and France saw inflation ease for the third consecutive month.
These divergent trends complicate the decision-making process following the ECB’s initial rate cut. Policymakers are already discussing the pace of subsequent steps, emphasizing that economic data will ultimately guide their decisions.
Lagarde has emphasized the ECB’s readiness to respond to new information, suggesting that the central bank cannot commit to a predetermined rate path even after the first rate cut.
🔥Stop trying to catch all movements in the market, trade only at the best confirmation trade setups
🎁 60% OFFER for Trading Signals 😍 GOING TO END – Get now: https://forexfib.com/offer/




