Understanding the Foreign Exchange Market
What is Forex?

Forex is a decentralized market where participants trade currencies. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across different financial centers worldwide. The primary players in the Forex market include banks, financial institutions, governments, corporations, and individual retail traders.
Major Currency Pairs

Currency pairs are the foundation of Forex trading. They represent the exchange rate between two currencies. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY, are the most heavily traded and offer high liquidity and tight spreads.
Factors Influencing Forex Prices
To master Forex trading, one must grasp the key factors that influence currency prices:
1. Economic Indicators

Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation rates, employment data, and other economic indicators can significantly impact currency values.
2. Central Bank Policies
 Decisions on interest rates and monetary policies made by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) in the United States or the European Central Bank (ECB), can cause substantial market movements.
Decisions on interest rates and monetary policies made by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) in the United States or the European Central Bank (ECB), can cause substantial market movements.
3. Geopolitical Events

Political instability, trade wars, and geopolitical tensions can create volatility in Forex markets.
4. Market Sentiment
 Traders’ perceptions and emotions can influence currency prices, leading to trends or reversals.
Traders’ perceptions and emotions can influence currency prices, leading to trends or reversals.
Building a Strong Foundation
1. Education and Research

Before diving into live trading, it’s crucial to invest time in education and research. Learn the fundamental concepts, technical analysis, and trading strategies employed by successful traders. Understand how economic events impact the Forex market and stay up-to-date with financial news.
2. Choose a Reliable Broker

Selecting the right Forex broker is paramount. Look for a regulated broker with a good reputation, low spreads, and robust trading platforms. Ensure they offer the currency pairs and trading tools that align with your trading style and goals.
3. Develop a Trading Plan

A well-defined trading plan is essential for success in the Forex market. Outline your trading goals, risk tolerance, preferred trading style (day trading, swing trading, or position trading), and risk management strategies. Stick to your plan and avoid impulsive decisions based on emotions.
Mastering Technical Analysis
1. Candlestick Patterns
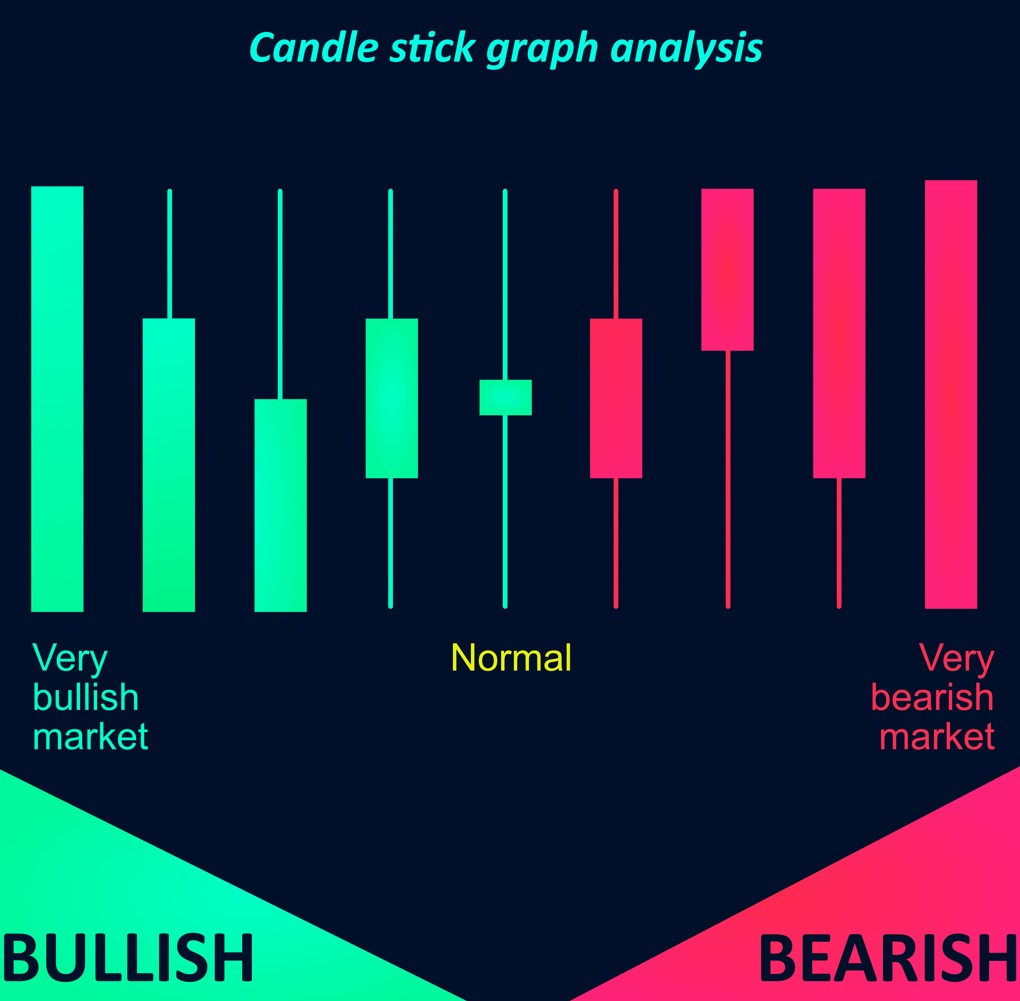 Candlestick charts provide valuable insights into price movements. Learn to identify common candlestick patterns, such as doji, hammer, and engulfing patterns, which can indicate potential trend reversals or continuations.
Candlestick charts provide valuable insights into price movements. Learn to identify common candlestick patterns, such as doji, hammer, and engulfing patterns, which can indicate potential trend reversals or continuations.
2. Support and Resistance
 Support and resistance levels are key price levels where the market tends to stall or reverse. Identifying these levels can help you make informed decisions on entry and exit points.
Support and resistance levels are key price levels where the market tends to stall or reverse. Identifying these levels can help you make informed decisions on entry and exit points.
3. Trendlines
 Trendlines connect successive higher lows or lower highs, visually representing the market’s direction. Understanding trendline analysis can assist in identifying trend strength and potential trend reversals.
Trendlines connect successive higher lows or lower highs, visually representing the market’s direction. Understanding trendline analysis can assist in identifying trend strength and potential trend reversals.
4. Indicators and Oscillators
 Utilize technical indicators and oscillators like Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to supplement your analysis. However, avoid cluttering your charts with too many indicators, as it can lead to confusion.
Utilize technical indicators and oscillators like Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to supplement your analysis. However, avoid cluttering your charts with too many indicators, as it can lead to confusion.
5. Fibonacci Retracements
 Fibonacci retracements help identify potential support and resistance levels based on the golden ratio. These levels often align with significant price movements.
Fibonacci retracements help identify potential support and resistance levels based on the golden ratio. These levels often align with significant price movements.
Mastering Fundamental Analysis
1. Economic Calendar
 Keep track of economic events using an economic calendar. Pay attention to high-impact events that can cause substantial market volatility.
Keep track of economic events using an economic calendar. Pay attention to high-impact events that can cause substantial market volatility.
2. Interest Rates and Central Bank Policies

Monitor central bank decisions on interest rates and monetary policies. Higher interest rates relative to other countries often strengthen a currency.
3. Trade Balances and Economic Data
 Trade balances and economic indicators, such as inflation rates and employment data, offer insights into a country’s economic health and can influence currency valuations.
Trade balances and economic indicators, such as inflation rates and employment data, offer insights into a country’s economic health and can influence currency valuations.
Developing Effective Trading Strategies
1. Scalping
 Scalping involves making quick trades to profit from small price movements. This strategy requires intense focus and discipline, as well as a reliable trading platform with low spreads.
Scalping involves making quick trades to profit from small price movements. This strategy requires intense focus and discipline, as well as a reliable trading platform with low spreads.
2. Day Trading
 Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day. Traders must develop a well-defined strategy, manage risks effectively, and avoid holding positions overnight.
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day. Traders must develop a well-defined strategy, manage risks effectively, and avoid holding positions overnight.
3. Swing Trading
 Swing trading aims to capture medium-term price movements over several days or weeks. Traders should focus on trends and employ risk management techniques.
Swing trading aims to capture medium-term price movements over several days or weeks. Traders should focus on trends and employ risk management techniques.
4. Carry Trading
 Carry trading involves profiting from the interest rate differential between two currencies. It requires a thorough understanding of economic factors and interest rate policies.
Carry trading involves profiting from the interest rate differential between two currencies. It requires a thorough understanding of economic factors and interest rate policies.
Risk Management
1. Position Sizing

Determine the appropriate position size for each trade based on your risk tolerance and the size of your trading account. Avoid risking a large percentage of your capital on a single trade.
2. Stop Losses

Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Place them at logical support or resistance levels, accounting for market volatility.
3. Emotion Management
 Controlling emotions, such as fear and greed, is crucial for successful trading. Stick to your trading plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions.
Controlling emotions, such as fear and greed, is crucial for successful trading. Stick to your trading plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions.
4. Learn from Mistakes

Trading is a continuous learning process. Analyze your trades, both successful and unsuccessful, to identify patterns and improve your trading strategy.
Psychological Aspects of Trading:
This section focuses on the psychological aspects of trading and the importance of emotional control.
1. Managing Emotions and Psychological Biases
 It discusses the impact of emotions and psychological biases on trading decisions and emphasizes the need for emotional control.
It discusses the impact of emotions and psychological biases on trading decisions and emphasizes the need for emotional control.
2. Developing Discipline and Patience
 This subsection highlights the importance of discipline and patience in following trading plans and strategies.
This subsection highlights the importance of discipline and patience in following trading plans and strategies.
3. Keeping a Trading Journal
 It emphasizes the benefits of maintaining a trading journal to track and analyze trades, learn from mistakes, and improve performance.
It emphasizes the benefits of maintaining a trading journal to track and analyze trades, learn from mistakes, and improve performance.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
Ongoing learning and adaptation are essential for success in the Forex market.
1. Staying Updated with Market News and Trends

This section emphasizes the importance of staying informed about market news, economic developments, and emerging trends.
2. Learning from Successful Traders
 It discusses the value of learning from experienced and successful traders and gaining insights from their strategies and experiences.
It discusses the value of learning from experienced and successful traders and gaining insights from their strategies and experiences.
3. Participating in Trading Communities and Educational Webinars

This subsection highlights the benefits of engaging with trading communities and attending educational webinars to broaden knowledge and exchange ideas.
Determining Timeframes and Trading Styles
This section deals with selecting appropriate timeframes and trading styles based on individual preferences and prevailing market conditions. Timeframes refer to the duration of a trade, which can range from short-term intraday trades (minutes to hours) to medium-term swing trades (a few days to weeks) or long-term position trades (weeks to months).
1.Trading styles
 It describe how a trader approaches the market and makes trading decisions. Some common trading styles include day trading, where traders open and close positions within the same trading day, and trend following, where traders try to identify and ride established market trends for an extended period.
It describe how a trader approaches the market and makes trading decisions. Some common trading styles include day trading, where traders open and close positions within the same trading day, and trend following, where traders try to identify and ride established market trends for an extended period.
2. The choice of timeframe and trading style
 It should align with a trader’s personality, risk tolerance, and the amount of time they can dedicate to trading. Additionally, market conditions may favor certain timeframes or styles, so traders should be flexible and adapt their approach accordingly.
It should align with a trader’s personality, risk tolerance, and the amount of time they can dedicate to trading. Additionally, market conditions may favor certain timeframes or styles, so traders should be flexible and adapt their approach accordingly.
Money Management Principles
Money management principles are crucial to the long-term success of any trader. This aspect of the trading plan focuses on how a trader manages their capital and risk. Key components of money management include:
1. Risk-Reward Ratio
 Evaluating the potential reward of a trade relative to the risk taken. Traders aim to have a positive risk-reward ratio, meaning they expect to make more on a winning trade than they would lose on a losing trade.
Evaluating the potential reward of a trade relative to the risk taken. Traders aim to have a positive risk-reward ratio, meaning they expect to make more on a winning trade than they would lose on a losing trade.
2. Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
 Setting specific price levels at which to exit a trade to limit potential losses (stop loss) and secure profits (take profit).
Setting specific price levels at which to exit a trade to limit potential losses (stop loss) and secure profits (take profit).
3. Capital Preservation

Implementing strategies to protect the trading capital from significant drawdowns and catastrophic losses. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Only use leverage that aligns with your risk tolerance and money management strategy.
4.Avoid Impulsive Trading
Do not make spontaneous decisions based on emotions or market hype. Stay disciplined and execute trades according to your trading plan.
5.Regular Assessment

Periodically review your trading performance, including gains, losses, and your adherence to the money management principles. Analyze your strengths and weaknesses to make necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of trading in the foreign exchange market is a challenging but rewarding endeavor. It requires a combination of technical expertise, fundamental knowledge, disciplined execution, and emotional intelligence. By building a strong foundation, employing effective trading strategies, and managing risks diligently, traders can increase their chances of success in the dynamic world of Forex trading. Remember, there is no shortcut to success, and continuous learning and practice are essential for staying ahead in this highly competitive market.



